Weight Loss Surgery Options
 Surgery for weight loss, also called bariatric surgery, has one primary aim – to reduce the amount of calories a patient can absorb, causing weight loss. This is done in one of two main ways.
Surgery for weight loss, also called bariatric surgery, has one primary aim – to reduce the amount of calories a patient can absorb, causing weight loss. This is done in one of two main ways.
The first is primarily by limiting the size of the stomach, so that less food can be consumed at any one time. The stomach normally holds about a liter of food at a time for processing and then passes this along. In the morbidly obese, the stomach can expand during a meal and hold even more, several liters in the obese.
The second type of surgery bypasses other parts of the digestive system.
Restrictive surgeries
In a restrictive type weight loss surgery, the objective is to reduce the amount of food someone can eat at any one time. The volume is cut from 1000 ml down to 30 – 50 ml. The ability to absorb calories isn’t impaired, only the amount of food it takes to fill the now restricted volume. Overeating is then physically impossible.
Gastric banding includes several types of surgery where a band or sleeve is placed around a section of the stomach to cut-off another section. These bands are adjustable – flexible balloon-like bands that have saline in them. Doctors can inject more saline to tighten the band or remove saline to loosen them. Two popular brand names of bands are Realize and Lap-Band.
Sleeve restriction is the same idea, but instead of physically restricting parts of the stomach, up to 75% of the stomach is removed. This type of restrictive surgery is permanent and not adjustable, since the unused parts of the stomach are no longer there.
Bypass surgeries
Although bypass surgeries also reduce stomach volume, they focus on preventing full absorption of the food taken in, rather than just limiting the amount. This second type of surgery reroutes the path food takes, skipping some parts of the digestive process.
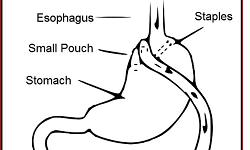
Gastric bypass combines surgical restriction (making the stomach smaller) and reconnecting the remaining stomach farther along the small intestine. Since most of the calories we consume are absorbed in the small intestine, this procedure both limits the amount that can be eaten and keeps the body from getting all the calories from what is consumed.
Biliopancreatic diversion is a type of bypass that surgically removes most of the stomach (70%) and bypasses even more of the small intestine. Otherwise, it is similar to a normal gastric bypass.
Risks and benefits
The primary benefit and the objective of weight loss surgery is a reduction in body mass index (BMI). This doesn’t come without risks however. Patients are at risk of not getting enough calories or nutrients. Diets have to be carefully monitored so this doesn’t happen. There are also other side effects, beyond the normal risks of surgery, especially in those procedures that reroute food passage. Sustained weight loss will depend, not just on the surgery, but lifestyle changes to reduce food consumption and promote healthy exercise.
 Eating Disorder Self Test. Take the EAT-26 self test to see if you might have eating disorder symptoms that might require professional evaluation. All answers are confidential.
Eating Disorder Self Test. Take the EAT-26 self test to see if you might have eating disorder symptoms that might require professional evaluation. All answers are confidential.